Improve the health of your jaw with a bone graft
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting is a surgery where the missing bone is replaced to allow for effective dental implants. With our advanced oral technology and procedures, we can even promote new bone growth in that location for optimal results.
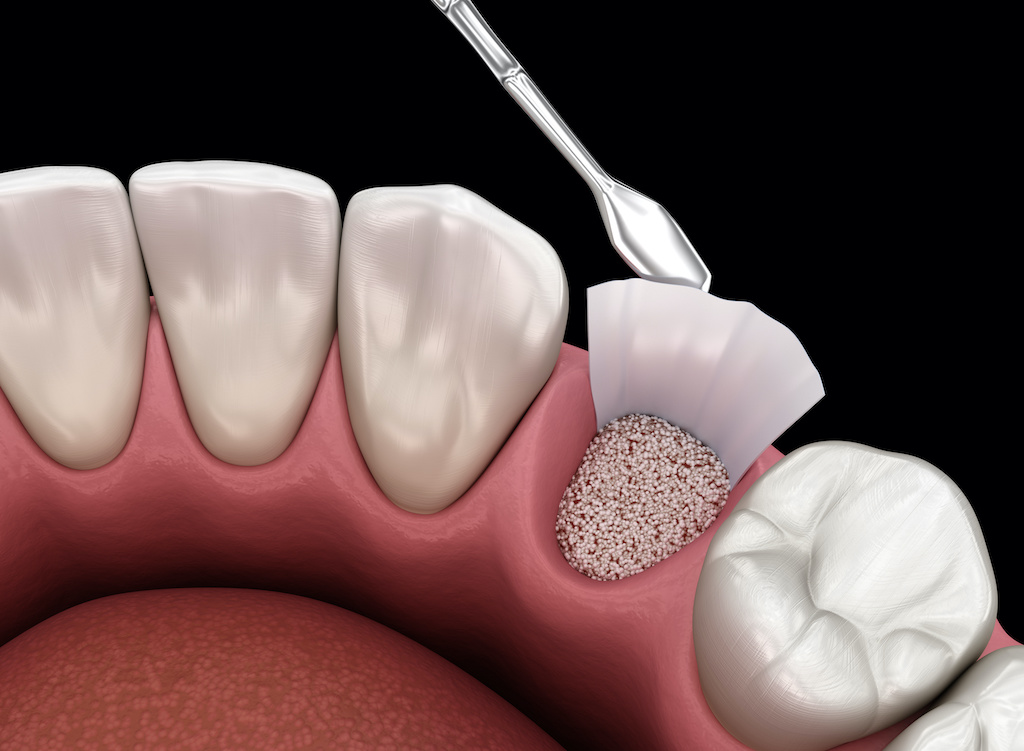
Types of bone grafts.
- Autogenous Bone Grafts
Also known as autograft, autogenous bone grafts involve taking samples from your bones located elsewhere and using these samples to rebuild the jawbone. Common harvest areas include the skull, hip, lower leg bone, jaw, and chin. The advantages of such a procedure include increased bone growth and the reduced chances of your body rejecting the bone, as it comes from your own body.
- Allogenic Bone
Allogenic bone (or allograft) is bone harvested from a cadaver. The bone is sterilized and then processed in a freeze-dried method. Allogenic bone grafts serve as a scaffold to guide healing of the jawbone.
- Xenogenic Bone
Xenogenic bone is extracted from another non-living species, like a cow. The bone is processed at high temperatures to sterilize the bone and reduce the risk of contamination and immune rejection. Xenogenic bone does not promote natural bone growth either. However, it does not require a second procedure such as the autograft.
Over a period of time, the jawbone associated with missing teeth atrophies or is reabsorbed. This often leaves a condition in which there is poor quality and quantity of bone suitable for placement of dental implants. In these situations, most patients are not candidates for placement of dental implants.
Today, we have the ability to grow bone where needed. This not only gives us the opportunity to place implants of proper length and width, it also gives us a chance to restore functionality and aesthetic appearance. These procedures can be often safely performed in the office under local or IV anesthesia.
Major Bone Grafting
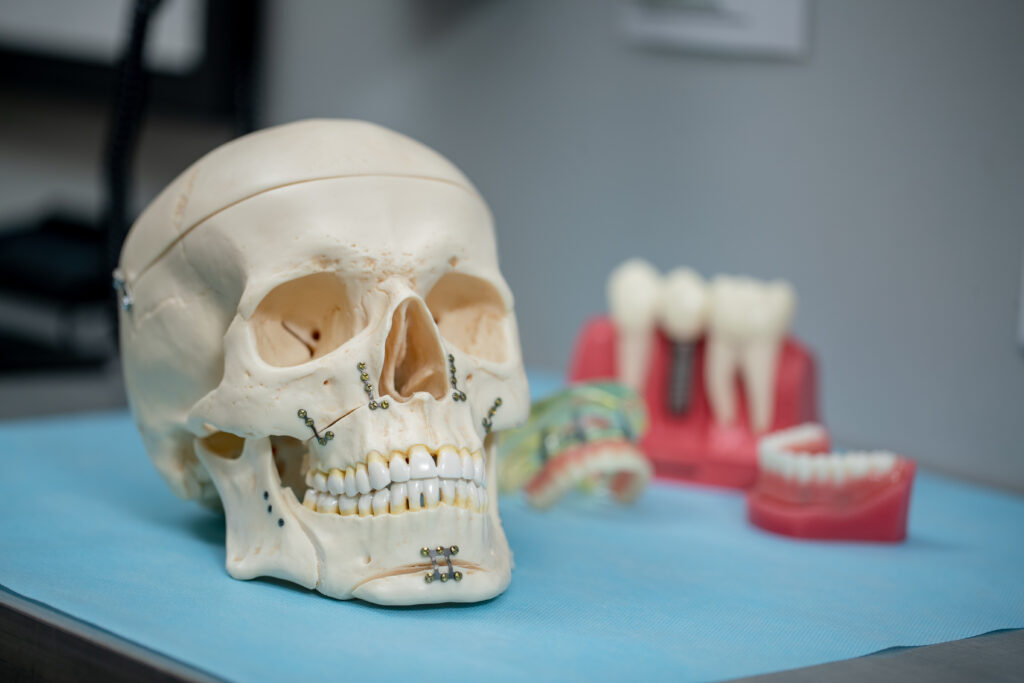
Bone grafting can repair implant sites with inadequate bone structure due to previous extractions, gum disease or injuries. The bone is either obtained from a tissue bank or your own bone is taken from the jaw, hip or tibia (below the knee). Sinus bone grafts are also performed to replace bone in the posterior upper jaw. In addition, special membranes may be utilized that dissolve under the gum and protect the bone graft and encourage bone regeneration. This is called guided bone regeneration or guided tissue regeneration.
Major bone grafts are typically performed to repair defects of the jaws. These defects may arise as a result of traumatic injuries, tumor surgery, or congenital defects. Large defects are repaired using the patients own bone. This bone is harvested from a number of different sites depending on the size of the defect. The skull (cranium), hip (iliac crest), and lateral knee (tibia), are common donor sites. These procedures are routinely performed in an operating room and require a hospital stay.
Get to know us.
At Washington Oral & Facial Surgery, we know how to help you. Our board-certified surgeons and expert staff can provide the care you need to relieve the discomfort you feel.


